Developing country
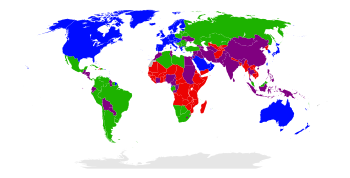


| 0.950 and Over 0.900–0.949 0.850–0.899 0.800–0.849 0.750–0.799 | 0.700–0.749 0.650–0.699 0.600–0.649 0.550–0.599 0.500–0.549 | 0.450–0.499 0.400–0.449 0.350–0.399 under 0.350 not available |
Developing country is a term generally used to describe a nation with a low level of material well-being (not to be confused with third world countries). Since no single definition of the term developed country is recognized internationally, the levels of development may vary widely within so-called developing countries, with some developing countries having high average standards of living.[1][2]
Countries with more advanced economies than other developing nations, but which have not yet fully demonstrated the signs of a developed country, are categorized under the term newly industrialized countries.[3][4][5][6]
Contents |
Definition
Kofi Annan, former Secretary General of the United Nations, defined a developed country as follows. "A developed country is one that allows all its citizens to enjoy a free and healthy life in a safe environment."[7] But according to the United Nations Statistics Division,
- There is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas in the United Nations system.[2]
And it notes that
- The designations "developed" and "developing" are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgment about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process.[8]
The UN also notes
- In common practice, Japan in Asia, Canada and the United States in northern America, Australia and New Zealand in Oceania, and Europe are considered "developed" regions or areas. In international trade statistics, the Southern African Customs Union is also treated as a developed region and Israel as a developed country; countries emerging from the former Yugoslavia, except for Slovenia, are treated as developing countries; and countries of eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States (code 172) in Europe are not included under either developed or developing regions.[2]
According to the classification from IMF before April 2004, all the countries of Eastern Europe (including Central European countries which still belongs to "Eastern Europe Group" in the UN institutions) as well as the former Soviet Union (U.S.S.R.) countries in Central Asia (Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan) and Mongolia, were not included under either developed or developing regions, but rather were referred to as "countries in transition"; however they are now widely regarded (in the international reports) as "developing countries". In the 21st century, the original Four Asian Tigers[9] regions (Hong Kong,[9][10] Singapore,[9][10] South Korea,[9][10][11][12] and Taiwan[9][10]), along with Cyprus,[10], Malta,[10] and Slovenia,[10] are considered "developed countries".
The IMF uses a flexible classification system that considers "(1) per capita income level, (2) export diversification—so oil exporters that have high per capita GDP would not make the advanced classification because around 70% of its exports are oil, and (3) degree of integration into the global financial system."[13]
The World Bank classifies countries into four income groups: -
- Low income countries have GNI per capita of US$975 or less.
- Lower middle income countries have GNI per capita of US$976–$3,855.
- Upper middle income countries have GNI per capita between US$3,856–$11,905.
- High income countries have GNI above $11,906.
"Income group: Economies are divided according to 2009 GNI per capita, calculated using the World Bank Atlas method. The groups are: low income, $995 or less; lower middle income, $996 - $3,945; upper middle income, $3,946 - $12,195; and high income, $12,196 or more." http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications
The World Bank classifies all low- and middle-income countries as developing but notes, "The use of the term is convenient; it is not intended to imply that all economies in the group are experiencing similar development or that other economies have reached a preferred or final stage of development. Classification by income does not necessarily reflect development status."[14]
Measure and concept of development
The development of a country is measured with statistical indexes such as income per capita (per person) (GDP), life expectancy, the rate of literacy, et cetera. The UN has developed the HDI, a compound indicator of the above statistics, to gauge the level of human development for countries where data is available.
Developing countries are in general countries which have not achieved a significant degree of industrialization relative to their populations, and which have, in most cases a medium to low standard of living. There is a strong correlation between low income and high population growth.
The terms utilized when discussing developing countries refer to the intent and to the constructs of those who utilize these terms. Other terms sometimes used are less developed countries (LDCs), least economically developed countries (LEDCs), "underdeveloped nations" or Third World nations, and "non-industrialized nations". Conversely, the opposite end of the spectrum is termed developed countries, most economically developed countries (MEDCs), First World nations and "industrialized nations".
To moderate the euphemistic aspect of the word developing, international organizations have started to use the term Less economically developed country (LEDCs) for the poorest nations which can in no sense be regarded as developing. That is, LEDCs are the poorest subset of LDCs. This may moderate against a belief that the standard of living across the entire developing world is the same.
The concept of the developing nation is found, under one term or another, in numerous theoretical systems having diverse orientations — for example, theories of decolonization, liberation theology, Marxism, anti-imperialism, and political economy.
Criticism of the term 'developing country'
There is criticism of the use of the term ‘developing country’. The term implies inferiority of a 'developing country' compared to a 'developed country', which many such countries dislike. It assumes a desire to ‘develop’ along the traditional 'Western' model of economic development which a few countries, such as Cuba, have chosen not to follow. Thus Cuba remains classed as 'developing' due to its low gross national income but has a lower infant mortality rate than the USA.[15]
The term 'developing' implies mobility and does not acknowledge that development may be in decline or static in some countries, particularly those southern African states worst affected by HIV/AIDS. In such cases, the term developing country may be considered a euphemism. The term implies homogeneity between such countries, which vary widely. The term also implies homogeneity within such countries when wealth (and health) of the most and least affluent groups varies widely.
In general, development entails a modern infrastructure (both physical and institutional), and a move away from low value added sectors such as agriculture and natural resource extraction. Developed countries, in comparison, usually have economic systems based on continuous, self-sustaining economic growth in the tertiary sector of the economy and quaternary sector of the economy and high material standards of living. However, there are notable exceptions, as some countries considered developed have a significant component of primary industries in their national economies, e.g. Norway, Canada, Australia. The USA and Western Europe have a very important agricultural sector, both are major players in international agricultural markets. Also, natural resource extraction can be a very profitable industry (high value added) e.g. oil extraction.
List of emerging and developing economies
The following are considered emerging and developing economies according to the International Monetary Fund's World Economic Outlook Report, April 2010.[16]
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria Angola
Angola Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan The Bahamas
The Bahamas Bahrain
Bahrain Bangladesh
Bangladesh Barbados
Barbados Belarus
Belarus Belize
Belize Benin
Benin Bhutan
Bhutan Bolivia
Bolivia Botswana
Botswana Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Brazil
Brazil Bulgaria
Bulgaria Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Burma
Burma Burundi
Burundi Cameroon
Cameroon Cape Verde
Cape Verde Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Chile
Chile China
China Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Costa Rica
Costa Rica Côte d'Ivoire
Côte d'Ivoire Croatia
Croatia Djibouti
Djibouti Dominica
Dominica Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt El Salvador
El Salvador Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Eritrea
Eritrea Estonia
Estonia Ethiopia
Ethiopia Fiji
Fiji Gabon
Gabon The Gambia
The Gambia Georgia
Georgia Ghana
Ghana Grenada
Grenada Guatemala
Guatemala Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Guyana
Guyana Haiti
Haiti Honduras
Honduras Hungary
Hungary Indonesia
Indonesia India
India Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Jamaica
Jamaica Jordan
Jordan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kenya
Kenya Kiribati
Kiribati Kuwait
Kuwait Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Laos
Laos Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Lesotho
Lesotho Liberia
Liberia Libya
Libya Lithuania
Lithuania Macedonia
Macedonia Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Marshall Islands[17]
Marshall Islands[17] Mauritania
Mauritania Mauritius
Mauritius Mexico
Mexico Federated States of Micronesia[17]
Federated States of Micronesia[17] Moldova
Moldova Mongolia
Mongolia Montenegro
Montenegro Morocco
Morocco Mozambique
Mozambique Namibia
Namibia Nauru
Nauru Nepal
Nepal Nicaragua
Nicaragua Niger
Niger Nigeria
Nigeria Oman
Oman Pakistan
Pakistan Palau[17]
Palau[17] Panama
Panama Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Philippines
Philippines Poland
Poland Qatar
Qatar Romania
Romania Russia
Russia Rwanda
Rwanda Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Samoa
Samoa São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe Senegal
Senegal Serbia
Serbia Seychelles
Seychelles Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands South Africa
South Africa Somalia
Somalia Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sudan
Sudan Suriname
Suriname Swaziland
Swaziland Syria
Syria Tajikistan
Tajikistan Tanzania
Tanzania Thailand
Thailand Timor-Leste
Timor-Leste Togo
Togo Tonga
Tonga Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Tuvalu
Tuvalu Uganda
Uganda Ukraine
Ukraine United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates Uruguay
Uruguay Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan Vanuatu
Vanuatu Venezuela
Venezuela Vietnam
Vietnam Yemen
Yemen Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Developing countries not listed by IMF
List of graduated developing economies (four Asian tigers and new Euro countries), now considered advanced economies
 Hong Kong (after 1997)
Hong Kong (after 1997) Singapore (after 1997)
Singapore (after 1997) South Korea (after 1997)
South Korea (after 1997) Taiwan (after 1997)
Taiwan (after 1997) Cyprus (after 2001)
Cyprus (after 2001) Slovenia (after 2007)
Slovenia (after 2007) Malta (after 2008)
Malta (after 2008) Czech Republic (after 2009)
Czech Republic (after 2009) Slovakia (after 2009)
Slovakia (after 2009)
Typology and names of countries
Countries are often loosely placed into four categories of development. Each category includes the countries listed in their respective article. The term "developing nation" is not a label to assign a specific, similar type of problem.
- Newly industrialized countries (NICs) are nations with economies more advanced and developed than those in the developing world, but not yet with the full signs of a developed country.[3][4][5][6] NIC is a category between developed and developing countries. It includes Brazil, China, India, Malaysia, Mexico, Philippines, South Africa, Thailand and Turkey.
- The Advanced Emerging Markets are Brazil, China, Czech Republic,[18] Hungary, India, Mexico, Poland, Russia, South Africa and Taiwan [19]
- Countries with long-term civil war or large-scale breakdown of rule of law ("failed states") (e.g. Democratic Republic of Congo, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Somalia) or non-development-oriented dictatorship (North Korea, Myanmar, Zimbabwe).
- Some developing countries have been classified as "Developed countries" such as Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Bahrain, Barbados, Brunei, Equatorial Guinea, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and Trinidad and Tobago by the World Bank.
References
- ↑ Sullivan, Arthur; Steven M. Sheffrin (2003). Economics: Principles in Action. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458: Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 471. ISBN 0-13-063085-3. http://www.pearsonschool.com/index.cfm?locator=PSZ3R9&PMDbSiteId=2781&PMDbSolutionId=6724&PMDbCategoryId=&PMDbProgramId=12881&level=4.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings (footnote C)". United Nations Statistics Division. revised 17 October 2008. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm#ftnc. Retrieved 2008-12-30.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Paweł Bożyk (2006). "Newly Industrialized Countries". Globalization and the Transformation of Foreign Economic Policy. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. ISBN 0-75-464638-6.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mauro F. Guillén (2003). "Multinationals, Ideology, and Organized Labor". The Limits of Convergence. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-69-111633-4.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Waugh, David (3rd edition 2000). "Manufacturing industries (chapter 19), World development (chapter 22)". Geography, An Integrated Approach. Nelson Thornes Ltd.. pp. 563, 576–579, 633, and 640. ISBN 0-17-444706-X.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Mankiw, N. Gregory (4th Edition 2007). Principles of Economics. ISBN 0-32-422472-9.
- ↑ http://www.unescap.org/unis/press/G_05_00.htm
- ↑ http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 http://www.businesspme.com/uk/articles/economics/78/East-Asian-Tigers-.html
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 IMF Advanced Economies List. World Economic Outlook, Database—WEO Groups and Aggregates Information, April 2009.
- ↑ http://travel.state.gov/travel/cis_pa_tw/cis/cis_1018.html
- ↑ http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/98c62f1c-850f-11dd-b148-0000779fd18c.html
- ↑ "Q. How does the WEO categorize advanced versus emerging and developing economies?". International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/faq.htm#q4b. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Country Classification". World Bank. http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/DATASTATISTICS/0,,contentMDK:20420458~menuPK:64133156~pagePK:64133150~piPK:64133175~theSitePK:239419,00.html. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
- ↑ "The World Factbook". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
- ↑ IMF Emerging and Developing Economies List. World Economic Outlook Database, April 2010.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 World Economic Outlook, International Monetary Fund, April 2009, second paragraph, lines 9–11.
- ↑ Possible change to Advanced Emerging.
- ↑ http://www.ftse.com/Indices/FTSE_Emerging_Markets/index.jsp.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||